Statistical Distributions
%matplotlib inline
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import scipy.stats as stats
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({
'font.size': 20.0,
'axes.titlesize': 'small',
'axes.labelsize': 'small',
'xtick.labelsize': 'small',
'ytick.labelsize': 'small'
})
def plot_continuous(dist):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharex=True, figsize=(15, 5))
# Plot hist
rvs = dist.rvs(size=1000)
ax[0].hist(rvs, alpha=0.2, histtype='stepfilled')
x=np.linspace(dist.ppf(0.01), dist.ppf(0.99), 50)
ax[0].plot(x, dist.pdf(x), '-', lw=2);
ax[0].set_title( dist.dist.name.title() + ' PDF')
ax[0].set_ylabel('p(X=x)')
# Plot cdf.
ax[1].plot(x, dist.cdf(x), '-', lw=2)
ax[1].set_title( dist.dist.name.title() + ' CDF')
ax[1].set_ylabel('p(X<=x)')
ax[1].set_xlabel('x');
return (fig, ax)
def plot_discrete(dist):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharex=True, figsize=(15, 5))
# Plot hist
rvs = dist.rvs(size=1000)
w = np.ones_like(rvs)/ float(len(rvs))
ax[0].hist(rvs, weights=w, alpha=0.2, histtype='stepfilled')
# Plot pmf.
k = np.arange(dist.ppf(0.01), dist.ppf(0.99)+1)
ax[0].plot(k, dist.pmf(k), 'bo', lw=2);
ax[0].set_title( dist.dist.name.title() + ' PMF')
ax[0].set_ylabel('p(X=k)')
# Plot cdf.
ax[1].plot(k, dist.cdf(k), 'bo', lw=2);
ax[1].set_title( dist.dist.name.title() + ' CDF')
ax[1].set_ylabel('p(X<=k)')
ax[1].set_xlabel('k');
return (fig, ax)
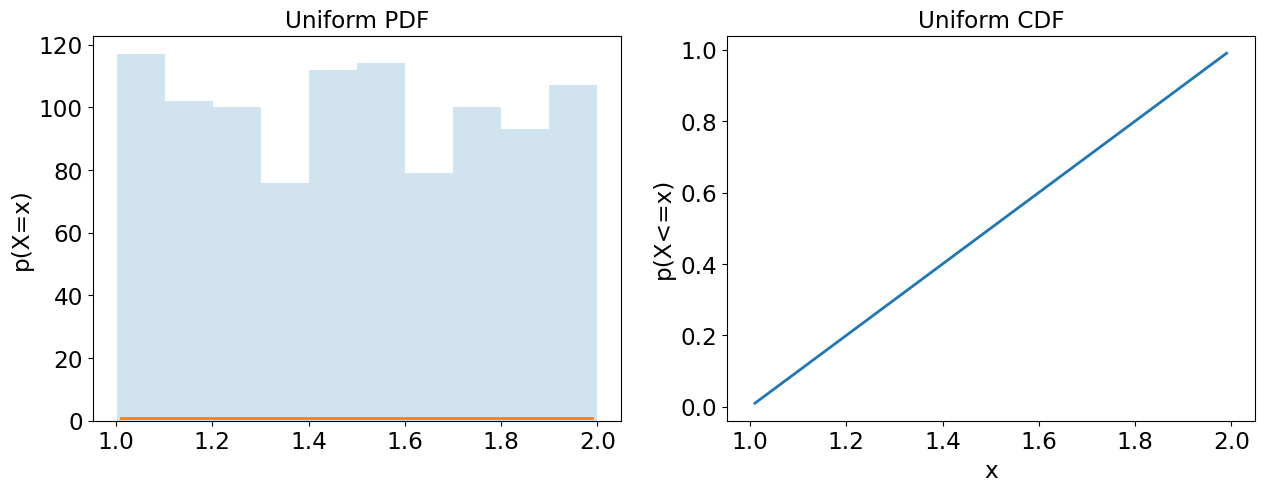
Uniform (Continuous)
#Models
Equally likely outcomes in the interval a to b, e.g. degrees between hour and minute hand.
#Parameters
aminimum value.bmaximum value.xobserved value.
a,b = 1,2
uniform = stats.uniform(loc=a, scale=b-a)
plot = plot_continuous(uniform)
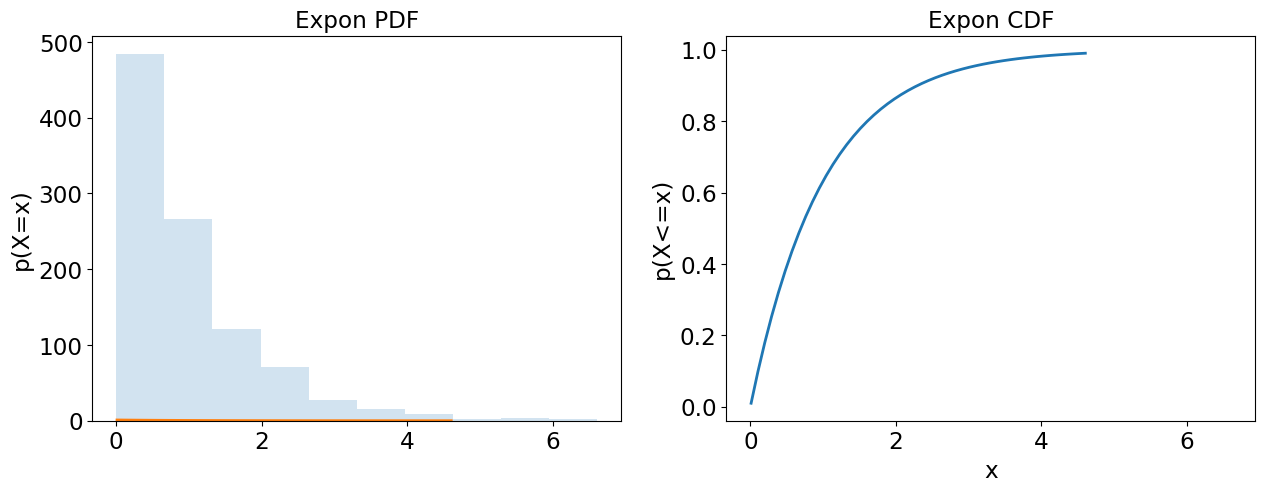
Exponential (Continuous)
#Models
Time between poisson events, e.g. time until taxi will pass street corner.
#Parameters
lambdaaverage number of independent events per interval.xobserved time between events.
lam = 1 # lambda
exponential = stats.expon(scale=1/lam)
plot = plot_continuous(exponential)
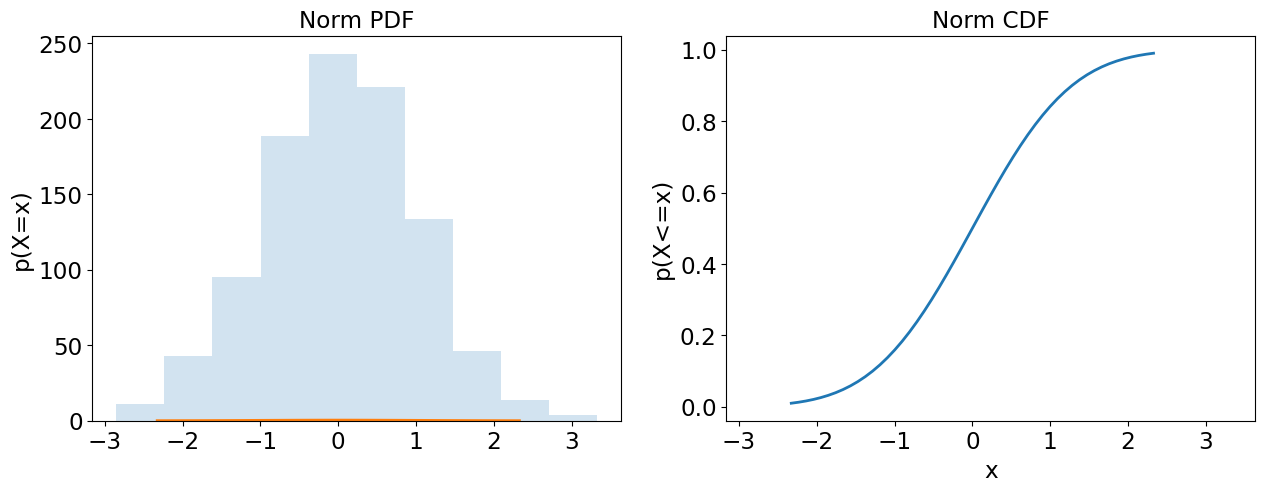
Gaussian (Continuous)
#Models
A bell curve, e.g. IQ score.
#Parameters
mumean or expectation.sigmastandard deviation.xobserved value.
mu, sigma = 0, 1
gaussian=stats.norm(loc=mu,scale=sigma)
plot = plot_continuous(gaussian)
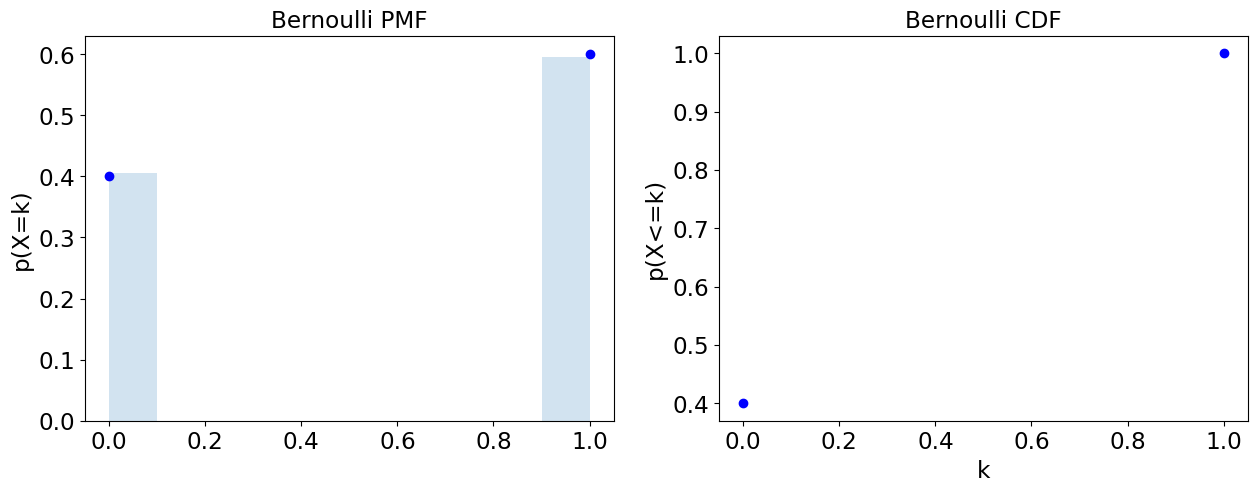
Bernoulli (Discrete)
#Models
One instance of a success or failure trial, e.g. (possibly unfair) coin toss.
#Parameters
pprobability of success.kfailure or success, i.e.{0,1}, observation.
bernoulli = stats.bernoulli(p=0.6)
plot = plot_discrete(bernoulli)
Geometric (Discrete)
#Models
Number of Bernoulli trials until first success, e.g. number of trials until coin flip turns out to be heads.
#Parameters
pprobability of success (each trial).kobserved trials until success.
geometric = stats.geom(p=0.5)
plot = plot_discrete(geometric)
Poisson (Discrete)
#Models
Number of events occurring in a fixed interval, e.g. number of taxis passing a street corner in a given hour (on avg. 10/hr).
#Parameters
lambdaaverage number of independent events per interval.kevents observed in an interval.
lam = 4 # lambda
poisson = stats.poisson(mu=lam)
plot = plot_discrete(poisson)
Binomial (Discrete)
#Models
Number of successes out of a number of Bernoulli trials with replacement., e.g. number of coin flips out of 100 that turn out to be heads.
#Parameters:
pprobability of success (each trial).nnumber of independent trials.kobserved number of successes
binomial=stats.binom(n=10,p=0.6);
plot = plot_discrete(binomial)
Weibull (Continuous)
#Models
Time between events when rate is not constant, e.g. time-to-failure when rate of failure increases or decreases over time.
Gamma (Continuous)
#Models
Waiting time between Poisson distributed events. Used when waiting times between events are relevant, e.g. aggregate insurance claims or the amount of rainfall accumulated in a reservoir.
Hypergeometric (Discrete)
#Models
Number of successes out of a number of success or failure trials without replacement, e.g. Number of times you draw a black ball from an urn of black and white balls without putting any back.